Flexible silicon solar breakthrough
Penn State University is reporting that for the first time, a silicon-based optical fiber with solar-cell capabilities has been developed that has been shown to be scalable to many meters in length. The research opens the door to the possibility of weaving together solar-cell silicon wires to create flexible, curved, or twisted solar fabrics. The findings by an international team of chemists, physicists, and engineers, led by John Badding, a professor of chemistry at Penn State University, will be posted by the journal Advanced Materials in an early online edition on 6 December 2012 and will be published on a future date in the journal's print edition.
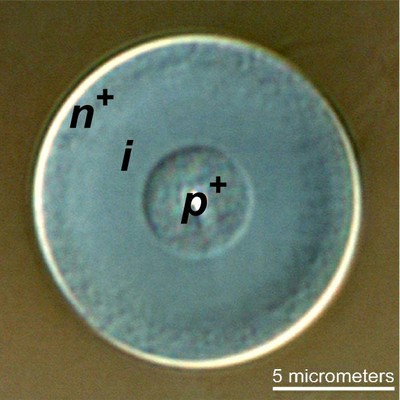
The team's new findings build on earlier work addressing the challenge of merging optical fibers with electronic chips -- silicon-based integrated circuits that serve as the building blocks for most semiconductor electronic devices such as solar cells, computers, and cell phones. Rather than merge a flat chip with a round optical fiber, the team found a way to build a new kind of optical fiber -- which is thinner than the width of a human hair -- with its own integrated electronic component, thereby bypassing the need to integrate fiber-optics with chips. To do this, they used high-pressure chemistry techniques to deposit semiconducting materials directly, layer by layer, into tiny holes in optical fibers.
Now, in their new research, the team members have used the same high-pressure chemistry techniques to make a fiber out of crystalline silicon semiconductor materials that can function as a solar cell -- a photovoltaic device that can generate electrical power by converting solar radiation into direct-current electricity. "Our goal is to extend high-performance electronic and solar-cell function to longer lengths and to more flexible forms. We already have made meters-long fibers but, in principle, our team's new method could be used to create bendable silicon solar-cell fibers of over 10 meters in length," Badding said. "Long, fiber-based solar cells give us the potential to do something we couldn't really do before: We can take the silicon fibers and weave them together into a fabric with a wide range of applications such as power generation, battery charging, chemical sensing, and biomedical devices."
Badding explained that one of the major limitations of portable electronics such as smart phones and iPads is short battery life. Solar-boosted batteries could help solve this problem. "A solar cell is usually made from a glass or plastic substrate onto which hydrogenated amorphous silicon has been grown," Badding explained. "Such a solar cell is created using an expensive piece of equipment called a PECVD reactor and the end result is something flat with little flexibility. But woven, fiber-based solar cells would be lightweight, flexible configurations that are portable, foldable, and even wearable." This material could then be connected to electronic devices to power them and charge their batteries. "The military especially is interested in designing wearable power sources for soldiers in the field," Badding added.
The team members believe that another advantage of flexibility in solar-cell materials is the possibility of collecting light energy at various angles. "A typical solar cell has only one flat surface," Badding said. "But a flexible, curved solar-cell fabric would not be as dependent upon where the light is coming from or where the sun is in the horizon and the time of day."
Pier J. A. Sazio of the University of Southampton in the United Kingdom and one of the team's leaders added, "Another intriguing property of these silicon-fiber devices is that as they are so compact, they can have a very fast response to visible laser light. In fact, we fabricated fiber-based photodetectors with a bandwidth of over 1.8 GHz."
In addition to Badding and Sazio, other researchers who contributed to this study include lead author Rongrui He, Todd D. Day, Mahesh Krishnamurthi, Justin R. Sparks, and Venkatraman Gopalan from Penn State.
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation, Penn State's Materials Research Institute Nano Fabrication Network, and the United Kingdom's Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).