Chemically Storing Solar Power
A photo-electrochemical cell has been developed at TU Wien (Vienna). It can chemically store the energy of ultraviolet light even at high temperatures.
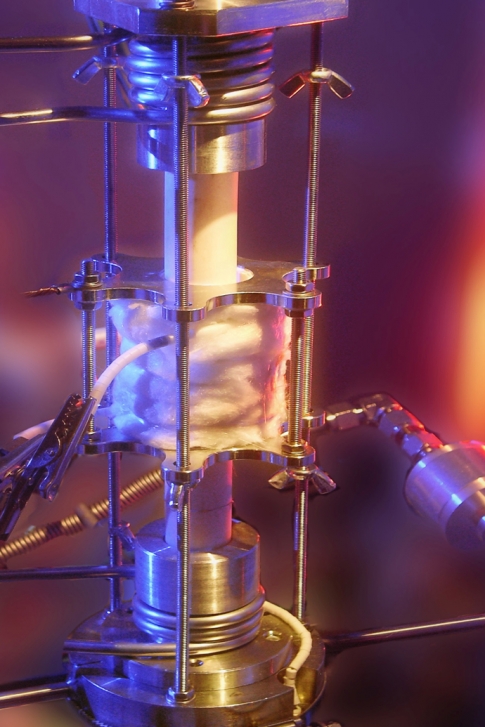
Heated reactor (TU Wien)
Nature shows us how it is done: Plants can absorb sunlight and store its energy chemically. Imitating this on large industrial scale, however, is difficult. Photovoltaics convert sunlight to electricity, but at high temperatures, the efficiency of solar cells decreases. Electrical energy can be used to produce hydrogen, which can then be stored "“ but the energy efficiency of this process is limited.
Scientists at TU Wien (Vienna) have now developed a new concept: By combining highly specialised new materials, they have managed to combine high temperature photovoltaics with an electrochemical cell. Ultraviolet light can be directly used to pump oxygen ions through a solid oxide electrolyte. The energy of the UV light is stored chemically. In the future, this method could also be used to split water into hydrogen and oxygen.
Special Materials for High Temperatures
As a student at TU Wien, Georg Brunauer started pondering possible combinations of photovoltaics and electrochemical storage. The feasibility of such a system depends crucially on whether it is able to work at high temperatures. "This would allow us to concentrate sunlight with mirrors and build large-scale plants with a high rate of efficiency", says Brunauer. Common photovoltaic cells, however, only work well up to 100°C. In a solar concentrator plant, much higher temperatures would be reached.
While working on his doctoral thesis, Brunauer managed to put his ideas into practice. The key to success was an unusual choice of materials. Instead of the ordinary silicon based photovoltaics, special metal oxides - so-called perovskites - were used. By combining several different metal oxides, Brunauer managed to assemble a cell which combines photovoltaics and electrochemistry. Several research partners at TU Wien contributed to the project. Georg Brunauer is a member of Prof. Karl Ponweiser's research team at the Institute for Energy Systems and Thermodynamics, Prof. Juergen Fleig's group (Chemical Technologies and Analytics) and the Institute for Atomic and Subatomic physics were involved as well.
Creating Voltage and Pumping Ions
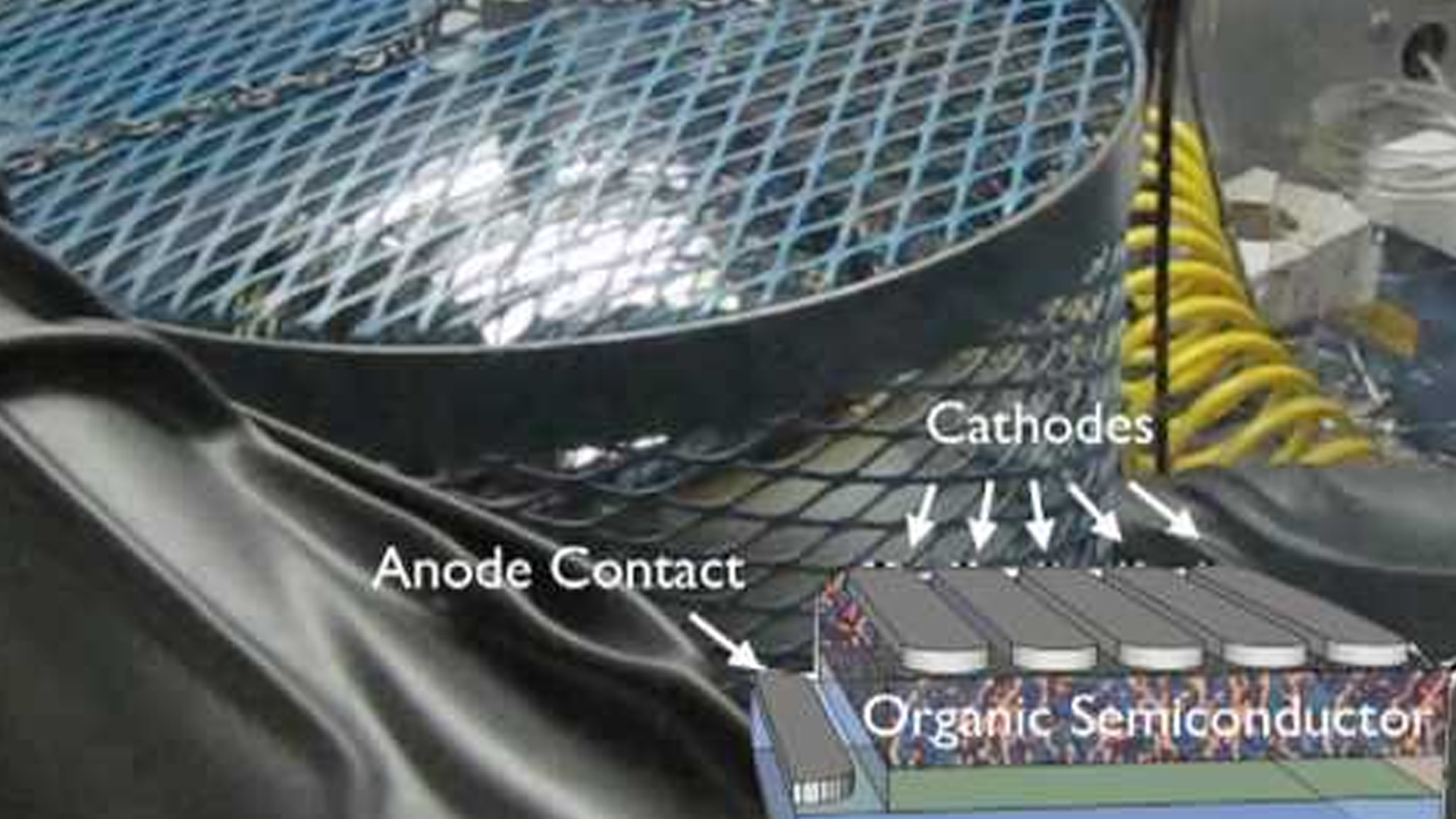
"Our cell consists of two different parts "“ a photoelectric part on top and an electrochemical part below", says Georg Brunauer. "In the upper layer, ultraviolet light creates free charge carriers, just like in a standard solar cell." The electrons in this layer are immediately removed and travel to the bottom layer of the electrochemical cell. Once there, these electrons are used to ionize oxygen to negative oxygen ions, which can then travel through a membrane in the electrochemical part of the cell.
"This is the crucial photoelectrochemical step, which we hope will lead to the possibility of splitting water and producing hydrogen", says Brunauer. In its first evolution step, the cell works as a UV-light driven oxygen pump. It yields an open-current voltage of up to 920 millivolts at a temperature of 400°C.
![]()
Photochemical cell: Light creates free charge carriers, oxygen (blue) is pumped through a membrane
The photoelectrochemical cell has now been presented in the journal "Advanced Functional Materials", but the research project continues. "We want to understand the origin of these effects by carrying out a few more experiments, and we hope that we will be able to improve our materials even further", says Brunauer. If the electrical power can be increased a slightly, the cell will be able to split water into oxygen and hydrogen. "This goal is within reach, now that we have shown that the cell is working", says Georg Brunauer. The concept is not only useful for the production of hydrogen, as it could also split carbon dioxide into carbon monoxide. The produced energy carried in the form of hydrogen and carbon monoxide can be used to synthesize fuels.
To make the leap from the university lab to an industrial prototype, Georg Brunauer has founded the startup company NOVAPECC. Together with TU Wien, he has filed several patents; Brunauer was supported by the University's Research and Transfer support, by the startup-support programme INITS and the Austrian Research Promotion Agency (FFG).