New material converts heat and light to energy
A multidisciplinary engineering team at the University of California, San Diego developed a new nanoparticle-based material for concentrating solar power plants designed to absorb and convert to heat more than 90 percent of the sunlight it captures. The new material can also withstand temperatures greater than 700 degrees Celsius and survive many years outdoors in spite of exposure to air and humidity. Their work, funded by the U.S. Department of Energy's SunShot program, was published recently in two separate articles in the journal Nano Energy.
By contrast, current solar absorber material functions at lower temperatures and needs to be overhauled almost every year for high temperature operations.
"We wanted to create a material that absorbs sunlight that doesn't let any of it escape. We want the black hole of sunlight," said Sungho Jin, a professor in the department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering. Jin, along with professor Zhaowei Liu of the department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Mechanical Engineering professor Renkun Chen, developed the Silicon boride-coated nanoshell material. They are all experts in functional materials engineering.
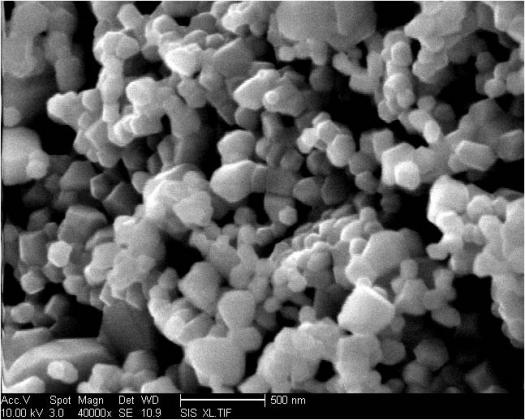
The novel material features a "multiscale" surface created by using particles of many sizes ranging from 10 nanometers to 10 micrometers. The multiscale structures can trap and absorb light which contributes to the material's high efficiency when operated at higher temperatures.
Concentrating solar power (CSP) is an emerging alternative clean energy market that produces approximately 3.5 gigawatts worth of power at power plants around the globe"”enough to power more than 2 million homes, with additional construction in progress to provide as much as 20 gigawatts of power in coming years. One of the technology's attractions is that it can be used to retrofit existing power plants that use coal or fossil fuels because it uses the same process to generate electricity from steam.
Traditional power plants burn coal or fossil fuels to create heat that evaporates water into steam. The steam turns a giant turbine that generates electricity from spinning magnets and conductor wire coils. CSP power plants create the steam needed to turn the turbine by using sunlight to heat molten salt. The molten salt can also be stored in thermal storage tanks overnight where it can continue to generate steam and electricity, 24 hours a day if desired, a significant advantage over photovoltaic systems that stop producing energy with the sunset.
One of the most common types of CSP systems uses more than 100,000 reflective mirrors to aim sunlight at a tower that has been spray painted with a light absorbing black paint material. The material is designed to maximize sun light absorption and minimize the loss of light that would naturally emit from the surface in the form of infrared radiation.
The UC San Diego team's combined expertise was used to develop, optimize and characterize a new material for this type of system over the past three years. Researchers included a group of UC San Diego graduate students in materials science and engineering, Justin Taekyoung Kim, Bryan VanSaders, and Jaeyun Moon, who recently joined the faculty of the University of Nevada, Las Vegas. The synthesized nanoshell material is spray-painted in Chen's lab onto a metal substrate for thermal and mechanical testing. The material's ability to absorb sunlight is measured in Liu's optics laboratory using a unique set of instruments that takes spectral measurements from visible light to infrared.
Current CSP plants are shut down about once a year to chip off the degraded sunlight absorbing material and reapply a new coating, which means no power generation while a replacement coating is applied and cured. That is why DOE's SunShot program challenged and supported UC San Diego research teams to come up with a material with a substantially longer life cycle, in addition to the higher operating temperature for enhanced energy conversion efficiency. The UC San Diego research team is aiming for many years of usage life, a feat they believe they are close to achieving.
Modelled after President Kennedy's moon landing program that inspired widespread interest in science and space exploration, then-Energy Secretary Steven P. Chu launched the Sunshot Initiative in 2010 with the goal of making solar power cost competitive with other means of producing electricity by 2020.
Image: Engineers at UC San Diego have developed a nanoparticle-based material for concentrating solar power plants that converts 90% of captured sunlight to heat. With particle sizes ranging from 10 nanometers to 10 micrometers, the multiscale structure traps and absorbs light more efficiently and at temperatures greater than 700 degrees Celsius.
Credit: Renkun Chen, mechanical engineering professor, UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering.