News Article
New approaches for hybrid solar cells
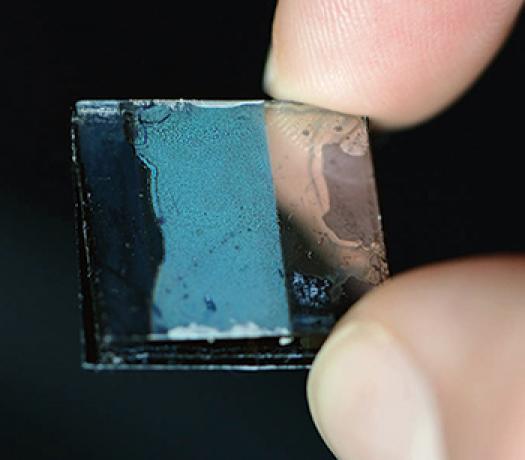
Using a new procedure researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the Ludwig Maximillians University of Munich (LMU) can now produce extremely thin and robust, yet highly porous semiconductor layers. A very promising material "“ for small, light-weight, flexible solar cells, for example, or electrodes improving the performance of rechargeable batteries.
The coating on the wafer that Professor Thomas Fässler, chair of Inorganic Chemistry with a Focus on Novel Materials at TU Munich, holds in his hands glitters like an opal. And it has amazing properties: It is hard as a crystal, exceptionally thin and "“ since it is highly porous "“ light as a feather. By integrating suitable organic polymers into the pores of the material, the scientists can custom tailor the electrical properties of the ensuing hybrid material. The design not only saves space, it also creates large interface surfaces that improve overall effectiveness.
"You can imagine our raw material as a porous scaffold with a structure akin to a honeycomb. The walls comprise inorganic, semiconducting germanium, which can produce and store electric charges. Since the honeycomb walls are extremely thin, charges can flow along short paths," explains Fässler.
The new design: bottom-up instead of top-down
But, to transform brittle, hard germanium into a flexible and porous layer the researchers had to apply a few tricks. Traditionally, etching processes are used to structure the surface of germanium. However, this top-down approach is difficult to control on an atomic level.
The new procedure solves this problem.
Together with his team, Fässler established a synthesis methodology to fabricate the desired structures very precisely and reproducibly. The raw material is germanium with atoms arranged in clusters of nine. Since these clusters are electrically charged, they repel each other as long as they are dissolved. Netting only takes place when the solvent is evaporated. This can be easily achieved by applying heat of 500°C or it can be chemically induced, by adding germanium chloride, for example. By using other chlorides like phosphorous chloride the germanium structures can be easily doped. This allows the researchers to directly adjust the properties of the resulting nanomaterials in a very targeted manner.

Tiny synthetic beads as nanotemplates
To give the germanium clusters the desired porous structure, the LMU researcher Dr. Dina Fattakhova-Rohlfing has developed a methodology to enable nanostructuring: Tiny polymer beads form three-dimensional templates in an initial step.
In the next step, the germanium-cluster solution fills the gaps between the beads. As soon as stable germanium networks have formed on the surface of the tiny beads, the templates are removed by applying heat. What remains is the highly porous nanofilm.
The deployed polymer beads have a diameter of 50 to 200 nanometers and form an opal structure. The germanium scaffold that emerges on the surface acts as a negative mold "“ an inverse opal structure is formed. Thus, the nanolayers glitter like an opal.
"The porous germanium alone has unique optical and electrical properties that many energy relevant applications can profit from," says LMU researcher Dr. Dina Fattakhova-Rohlfing, who, in collaboration with Fässler, developed the material. "Beyond that, we can fill the pores with a wide variety of functional materials, thereby creating a broad range of novel hybrid materials."
Nanolayers pave the road to portable photovoltaic solutions
"When combined with polymers, porous germanium structures are suitable for the development of a new generation of stable, extremely light-weight and flexible solar cells that can charge mobile phones, cameras and laptops while on the road," explains the physicist Peter Mueller-Buschbaum, professor of functional materials at TU Munich.
Manufacturers around the world are on the lookout for light-weight and robust materials to use in portable solar cells. To date they have used primarily organic compounds, which are sensitive and have relatively short lifetimes. Heat and light decompose the polymers and cause the performance to degrade. Here, the thin but robust germanium hybrid layers provide a real alternative.
Nanolayers for new battery systems
Next, the researchers want to use the new technology to manufacture highly porous silicon layers. The layers are currently being tested as anodes for rechargeable batteries. They could conceivably replace the graphite layers currently used in batteries to improve their capacity.
The research was funded by the "Solar Technologies Go Hybrid" program of the Bavarian State Ministry of Science, in the context of the excellence cluster "Nanosystems Initiative Munich (NIM), the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the Center for Nanosciences (CeNS).
The coating on the wafer that Professor Thomas Fässler, chair of Inorganic Chemistry with a Focus on Novel Materials at TU Munich, holds in his hands glitters like an opal. And it has amazing properties: It is hard as a crystal, exceptionally thin and "“ since it is highly porous "“ light as a feather. By integrating suitable organic polymers into the pores of the material, the scientists can custom tailor the electrical properties of the ensuing hybrid material. The design not only saves space, it also creates large interface surfaces that improve overall effectiveness.
"You can imagine our raw material as a porous scaffold with a structure akin to a honeycomb. The walls comprise inorganic, semiconducting germanium, which can produce and store electric charges. Since the honeycomb walls are extremely thin, charges can flow along short paths," explains Fässler.
The new design: bottom-up instead of top-down
But, to transform brittle, hard germanium into a flexible and porous layer the researchers had to apply a few tricks. Traditionally, etching processes are used to structure the surface of germanium. However, this top-down approach is difficult to control on an atomic level.
The new procedure solves this problem.
Together with his team, Fässler established a synthesis methodology to fabricate the desired structures very precisely and reproducibly. The raw material is germanium with atoms arranged in clusters of nine. Since these clusters are electrically charged, they repel each other as long as they are dissolved. Netting only takes place when the solvent is evaporated. This can be easily achieved by applying heat of 500°C or it can be chemically induced, by adding germanium chloride, for example. By using other chlorides like phosphorous chloride the germanium structures can be easily doped. This allows the researchers to directly adjust the properties of the resulting nanomaterials in a very targeted manner.
Tiny synthetic beads as nanotemplates
To give the germanium clusters the desired porous structure, the LMU researcher Dr. Dina Fattakhova-Rohlfing has developed a methodology to enable nanostructuring: Tiny polymer beads form three-dimensional templates in an initial step.
In the next step, the germanium-cluster solution fills the gaps between the beads. As soon as stable germanium networks have formed on the surface of the tiny beads, the templates are removed by applying heat. What remains is the highly porous nanofilm.
The deployed polymer beads have a diameter of 50 to 200 nanometers and form an opal structure. The germanium scaffold that emerges on the surface acts as a negative mold "“ an inverse opal structure is formed. Thus, the nanolayers glitter like an opal.
"The porous germanium alone has unique optical and electrical properties that many energy relevant applications can profit from," says LMU researcher Dr. Dina Fattakhova-Rohlfing, who, in collaboration with Fässler, developed the material. "Beyond that, we can fill the pores with a wide variety of functional materials, thereby creating a broad range of novel hybrid materials."
Nanolayers pave the road to portable photovoltaic solutions
"When combined with polymers, porous germanium structures are suitable for the development of a new generation of stable, extremely light-weight and flexible solar cells that can charge mobile phones, cameras and laptops while on the road," explains the physicist Peter Mueller-Buschbaum, professor of functional materials at TU Munich.
Manufacturers around the world are on the lookout for light-weight and robust materials to use in portable solar cells. To date they have used primarily organic compounds, which are sensitive and have relatively short lifetimes. Heat and light decompose the polymers and cause the performance to degrade. Here, the thin but robust germanium hybrid layers provide a real alternative.
Nanolayers for new battery systems
Next, the researchers want to use the new technology to manufacture highly porous silicon layers. The layers are currently being tested as anodes for rechargeable batteries. They could conceivably replace the graphite layers currently used in batteries to improve their capacity.
The research was funded by the "Solar Technologies Go Hybrid" program of the Bavarian State Ministry of Science, in the context of the excellence cluster "Nanosystems Initiative Munich (NIM), the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the Center for Nanosciences (CeNS).